Process and Information on Suction Aspiration
🏥 Abortion Methods: What Do I Need to Know? — Quiz
- Vacuum aspiration, also known as suction aspiration or aspiration curettage, is a surgical abortion method.
- This is an outpatient surgery performed under general or local anaesthesia. It takes about 10–15 minutes.
- The cervix is dilated, and the embryo is suctioned out.
Continue reading to find information on the procedure, possible risk factors and other considerations.
Abortion Methods: What Do I Need to Know? — Quiz
Wondering what method to choose? Answer three multiple-choice questions about your situation and receive a professional evaluation within seconds on your screen.
What is Vacuum Aspiration?
Aspiration, also known as vacuum aspiration or suction abortion, is the most common in-clinic abortion method worldwide.
Overview of important facts:
Vacuum aspiration is a type of surgical abortion. It is usually performed between the 5th and 16th week of pregnancy.
Aspiration is an outpatient procedure that takes 10–15 minutes.
It is most commonly performed under sedation but can also be done under local anaesthesia, which is applied to the cervix.
More information:
Step-by-Step: Vacuum Aspiration
Before the Procedure
If the pregnant woman has never given birth, she may be given prostaglandins (usually Misoprostol or Cytotec) a few hours before the procedure. These hormones, which cause the cervix to ripen, are administered vaginally as a tablet or gel. Hormone injections are rarely used.
Immediately before the procedure, an anaesthetist administers the sedation or general or local anaesthesia, as is routine for any surgery.
During the Procedure
The procedure itself takes about ten to fifteen minutes. The doctor proceeds as follows:
- The cervical opening is dilated with special rods (i.e. Hegar dilators).
- A flexible plastic tube is then inserted through the dilated cervix and into the uterus. This is connected to either a suction machine (Electrical Vacuum Aspiration; EVA) or a hand pump (Manual Vacuum Aspiration; MVA). While an electrical pump (EVA) is used in 90% of cases, using a handheld syringe (MVA) is equally effective.
- Via suction, the uterus is emptied of the embryo and the placenta.
- After the procedure, the physician examines the extracted material to ensure the abortion is complete. He may also use ultrasound to check whether the uterus is empty. If there is a remnant, it is removed by repeating a suction aspiration or by performing a D&C to avoid infection.
- Antibiotics are commonly given on the day of operation to prevent infection.
After the Procedure
About two hours after the procedure, the woman is discharged. If any sedation was used, the patient will not be permitted to drive for the remainder of the day. It is also recommended that someone stay with her overnight. A follow-up visit is recommended seven to 14 days after an aspiration abortion.
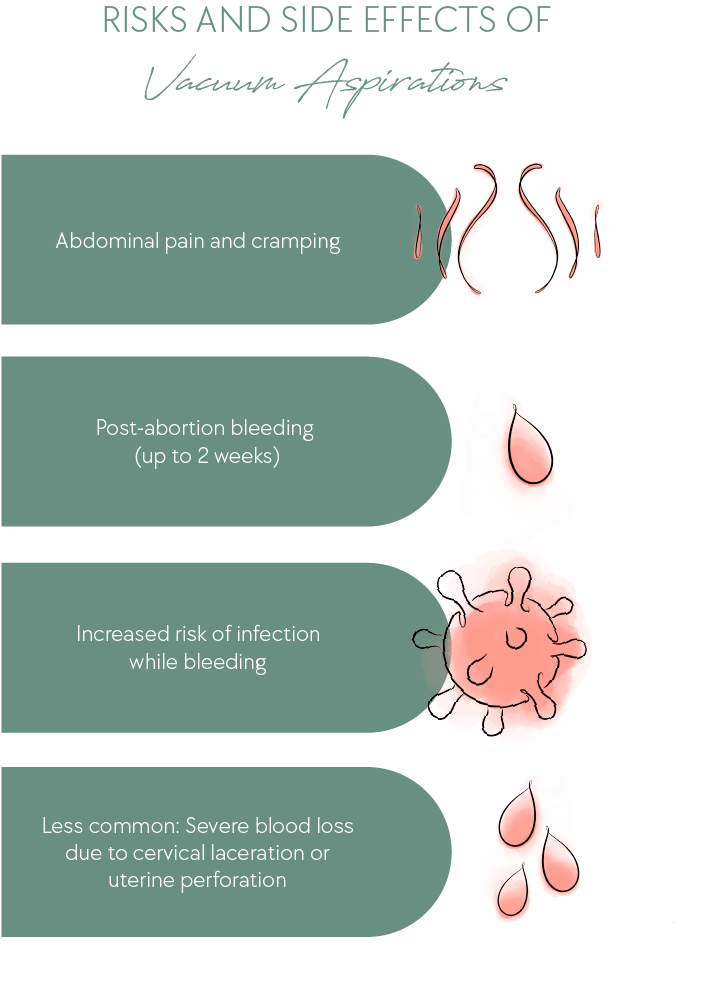
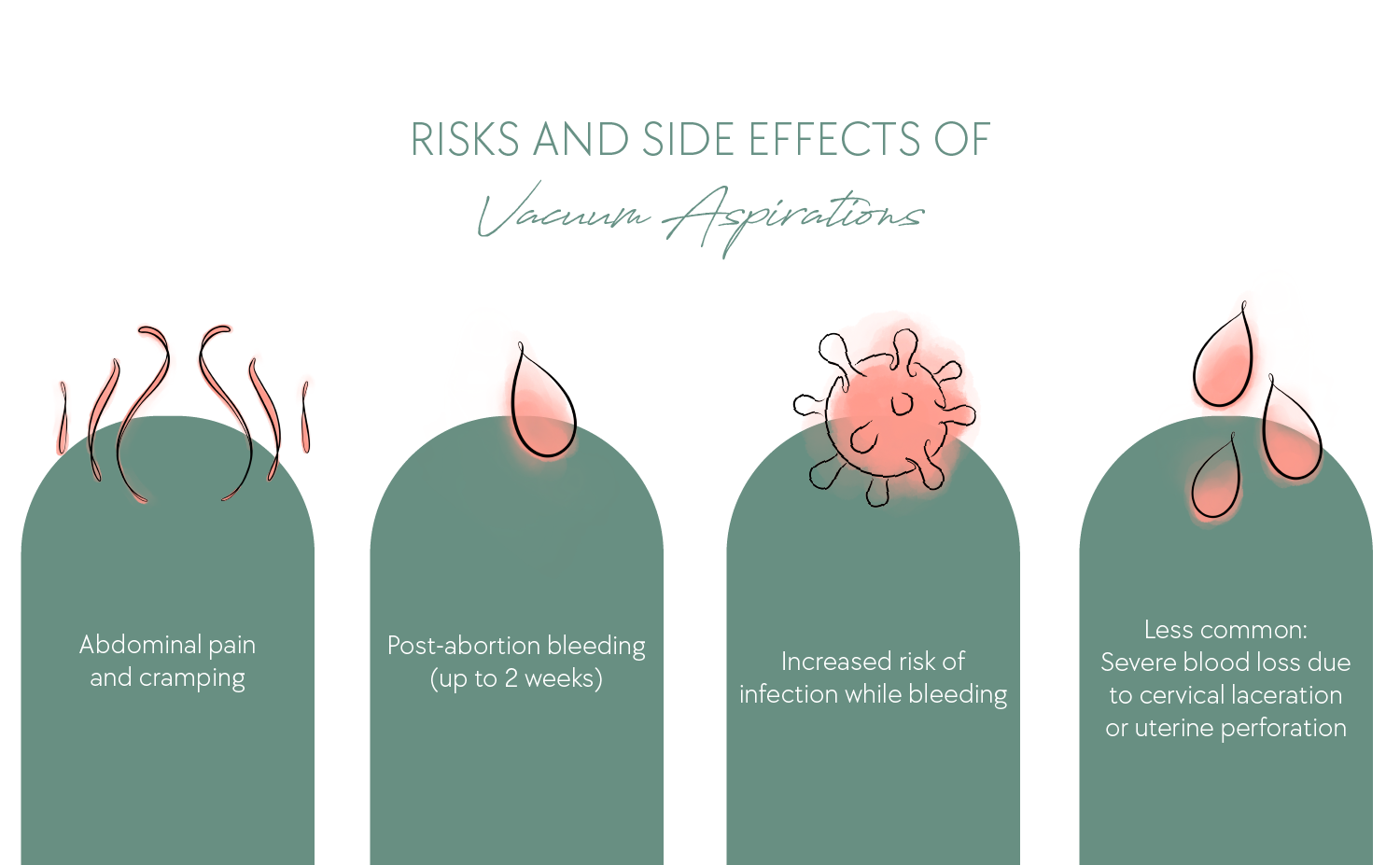
How Safe Is Vacuum Aspiration?
Suction abortions tend to have fewer complications than D&Cs or D&Es. Nevertheless, even suction aspirations have certain risks and side effects. Before the procedure, the doctor will discuss potential risks with you.
-
🛤 Could an abortion affect me long term? — Test and information on risks and emotional impact of abortion.
Where Do I Go from Here?
Are you pregnant and unsure what to do? Your quest for answers has led you to research various abortion methods.
Apart from the informational aspect, you are most likely dealing with a whole other set of feelings and concerns. You may feel as if your entire world is breaking apart, and you are wondering where to go from here.
We created a judgement-free environment where you can make a decision that is just right for you. Why not give it a try?
Take one of our free online tests and receive an immediate evaluation:
- ⚖️ Abortion: yes or no? — Take the Abortion Test
- ⛑ Unintended pregnancy? — Take the First Aid Test
- 💪 What are my strengths? — Take the Strengths Finder Test
- 🏥 Abortion methods — What do I need to know? Test
FAQs
-
Vacuum aspiration (aka, suction abortion) is an outpatient surgical abortion method. Internationally, this is the most common abortion procedure. The name says it all: the embryo and placenta are drawn out of the uterus via vacuum suction.
-
Before the procedure, a prostaglandin is usually given to relax the cervix. During the procedure, which is performed under local anaesthesia or sedation, a pump is used to suction out the embryo and placenta. Post-surgery, the woman will need someone to drive her home and stay with her.
-
Very few complications are associated with this type of surgical abortion procedure. Information on possible risks and side effects (of the procedure and sedation) is provided during the pre-op interview. A follow-up appointment after seven to 14 days is necessary in order to determine whether any part of the embryo remained in the uterus.



















